Author: Queen of Objects (Peng Chao)
This article is reproduced in the Public Number Internet of Think Tank
Reading Guide
In the future Internet of Things market, the role of "all things operator" will become increasingly prominent and occupy a considerable value. Scenario-centric, "running everything" and profit from it will be an important business model. It is difficult to say the full meaning of an article, so this article will give an extended interpretation of "all operators".

In the previous article, Two Business Models in which Internet of Things Enterprises Break Out Successfully in the Era of Billions, I mentioned that the core competitive points and bottlenecks of the current Internet of Things have shifted from technical solutions to application competition and business models. Both Internet of Things product application providers, Internet of Things data analysis service providers, and Internet of Things connection operators need to pay attention to product experience and continuous operation.
That is, in the future Internet of Things market, the role of "all things operator" will become increasingly prominent and occupy a considerable value. Scenario-centric, "running everything" and profit from it will be an important business model. It is difficult to say the full meaning of an article, so this article will give an extended interpretation of "all operators":
-
What is a Universal Operator? Why do I want to discuss operations at the current node?
-
Will NB-IoT be a pioneer or a pioneer in everything?
-
Why will the era of all operators be "completely different"?

5G is the key enabling technology for everything operation
Why is the age of Universal Operators imminent?
From the perspective of industrial infrastructure upgrade, when the underlying technology develops to a certain stage, new opportunities will gradually emerge, and the "technology fuse" triggering this change is 5G.
Did you notice that the latest news about 5G pops up almost every day? Recently, for example, according to foreign media reports, Germany has decided to allocate the entire C-band to 5G, that is, the 3.4 GHz-3.8 GHz spectrum. Car manufacturers such as BMW, Daimler and Volkswagen have expressed their interest in building and operating a local 5G network to the German Spectrum Authority BNA. For security and controllability reasons, some large industrial enterprises are also exploring the 5G private network layout, replacing and reconstructing wired Industrial Ethernet in their factories with ultra-low latency 5G NR links. The German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence DFKI, SKF, Ericsson and other organizations have tried 5G industrial applications, which have achieved good results in the verification phase.
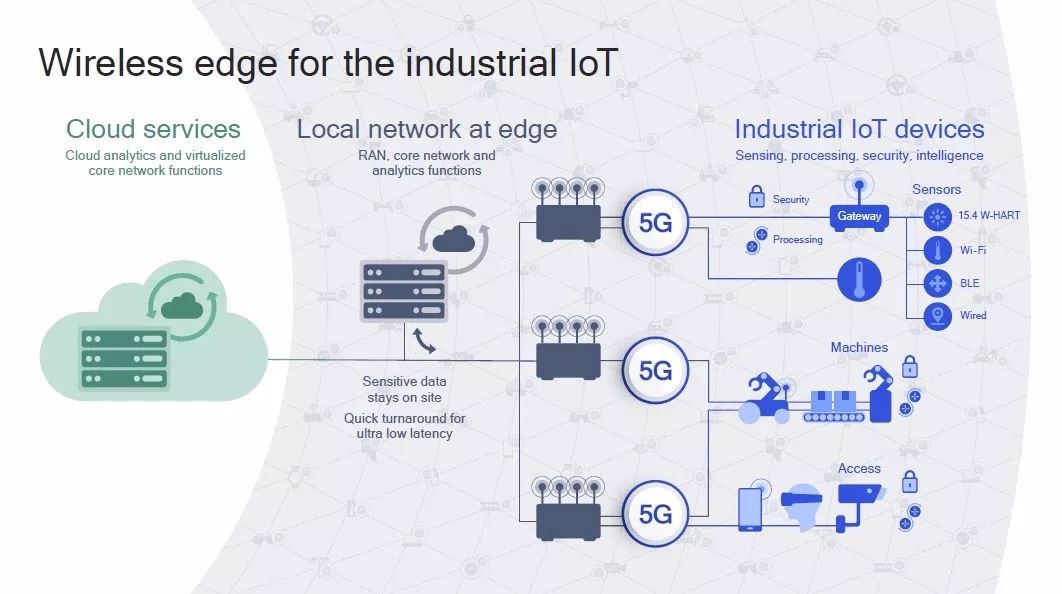
If the previous mobile communication mainly solved the communication problem between people, with the arrival of 5G, most of the eyes of operators and their upstream and downstream are attracted by the interconnection of everything, and it is expected that hundreds of billions of devices will be connected to the 5G network. Operators have started laying out 5G infrastructure. According to Ericsson, GSMA and other agencies, auto-driving cars, unmanned aerial vehicles, virtual reality, manufacturing (...) is just the beginning of 5G applications, which will drive the explosion of smart devices and change our lives completely.
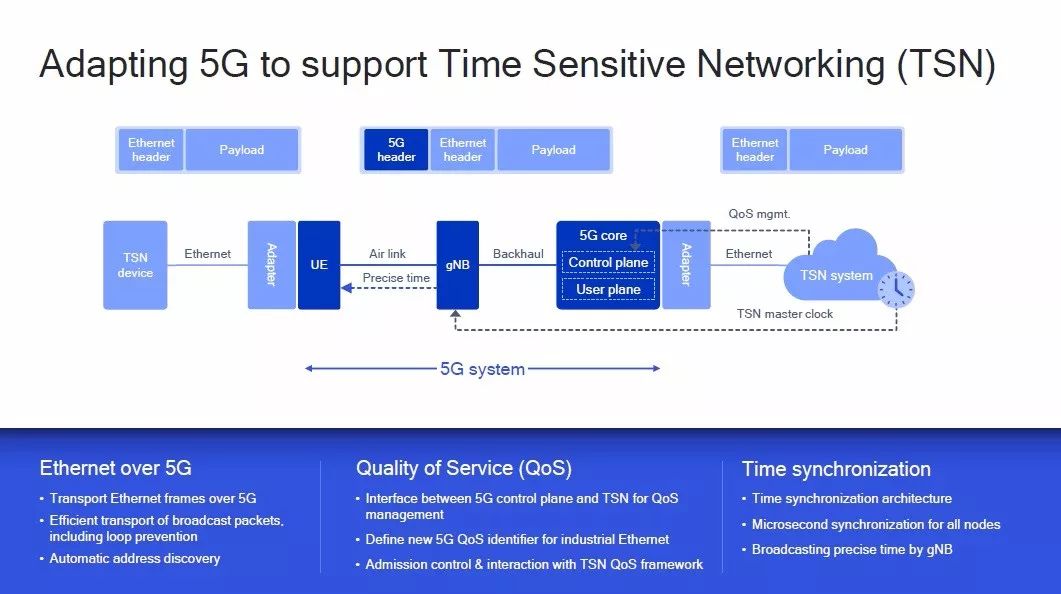
The technical features and application advantages of 5G networks must be well known to you: not only will they result in significant improvements in data rates, but also in latency and connection quality. With the promotion of 3GPP, NB-IoT/eMTC and its evolution technology have been incorporated into 5G family, which ensures the smooth upgrade of NB-IoT/eMTC to the future 5G network. In the industrial field, 5G is actively integrating with time-sensitive network TSN to meet the requirements of ultra-low latency, accurate real-time performance and high reliability in the industrial field.
It is predicted that by 2025 China will have 430 million 5G connections, accounting for one-third of the global total. The rapid growth of traffic has triggered the explosion of large-scale data applications, which has opened up more uses for Internet of Things, Artificial Intelligence, Business Intelligence and other applications relying on large data resources for intelligent decision-making.
In the previous article, I mentioned that there are three types of Internet of Things application and service enterprises: Internet of Things product application providers, Internet of Things data analysis service providers, and Internet of Things connection operators. These companies may be the embryonic form of the Universal Operators.
What is a Universal Operator?
When an Internet of Things enterprise no longer only pursues selling products to users, but also provides various kinds of additional services on the original basis, and continuously generates new service content and income methods, it has the business basis to become a "world operator".
"Universal Operators" may be a new term for you. In fact, their operational logic has been spread throughout the smart network automotive, smart city, industrial site, smart logistics, smart building and other industries and consumer markets. This new type of "all things operator", on the one hand, depends on the adoption of Internet of Things technology to transform the original industry, on the other hand, coincides with the additional dividends of the Internet of Things era, around which a new industrial ecology is built, and through edge computing and intelligent analysis capabilities, an innovative service network is created.
Universal Operators can offer leased services to enterprises or individual customers based on the differentiated end-to-end network architecture and infrastructure resources, providing services such as acceptance, opening, billing, fee collection, operation and maintenance. Based on the data collected by the Internet of Things, we can also tap into its commercial value, optimize production, remote first aid or resource allocation, and maximize the value of various infrastructure and technical capabilities such as "number, network, cloud".

The foundation of everything operation is thought transformation
The biggest difficulty and value point of the Internet of Things is not the technical solution, but the business model. The shaping of business model is not limited to the previous accumulation, but more important is the change of thinking.
In the 5G era, the underlying infrastructure will be further opened, providing convenience for free combination and arrangement, realizing rational arrangement of resources and flexible invocation of capabilities. These basic technical improvements are combined to achieve "network resource capability". The underlying communication technology is decoupled and improved. From then on, the upper application developers are no longer constrained by the communication network specialty and boundary, and take the demand as the starting point, let the underlying resources be used by me, and achieve a win-win situation.

For 5G, the most important thing is to find the path of business value, especially growth and change, so that operators and industries can work together to develop 5G. One important point is cost.
On the one hand, it is the cost for telecommunication operators to make network resources capable. Communication equipment manufacturers are developing based on communication standards with long periods, high cost of change and stability requirements. Thresholds make it impossible for them to iterate through trial and error like Internet companies. If the communication resources are combined into communication capabilities with long period, high cost and complex operation, it will be difficult to popularize them on a large scale, let alone commercial realizations, even if the functions can be achieved in theory.
The other is the cost of deploying end-to-end 5G devices and services in all industries. Hardware costs such as chips, storage, sensors are becoming cheaper as Moore's Law evolves, but the cost of installing, debugging, and operating various devices will not continue to fall according to Moore's Law. At present, the deployment cost of many devices has exceeded the hardware itself. Even if it is much cheaper to retrofit a stock device than to replace it with a new one, the installation workload and cost must be considered.
The focus of everything operation is not on "connection", but on "operation". The NB-IoT experience and lessons may provide some reference for the development of all operators. In the article "NB-IoT, the backbone of the Internet of Things in the future, or can't be supported?", the author pointed out sharply that gas meters and water meters are the main force of NB-IoT shipment at present, and other applications are more or less congenitally inadequate. For example, the lack of a strong policy push for smoke detectors, the cost of well cover monitors is not cost-effective, the smart trash can is a big problem, no one pays for tree and green monitoring, and the poor user experience of electric vehicle GPS locators.
Most NB-IoT projects originate from government-sponsored tenders or government subsidies. This is a good way to guide the development of industries in the early stages, but government projects cannot support an industry. Besides social benefits, economic benefits should also be considered. Creating sustainable cash returns by meeting real needs is the basis for the healthy development of industries.
Therefore, when using NB-IoT to connect various devices, the operational value of the device itself must be considered. When Internet companies provide user services, and make a distinction between high net value groups and ordinary people, frequent travelers and first-time users, Internet of Things enterprises should make a reasonable design of all things operation priority according to the business value created after the devices are connected to the network.
For example, based on the same communication technology as NB-IoT, it is possible to draw a cycling thermogram based on shared bicycle usage data, help the government solve the last kilometer problem for citizens, assist the transportation department in predicting congested sections, or help supermarkets choose store locations. The number of connections may not be the most, but the value of operation is significantly higher than that of street lights and well covers.
Therefore, when all operators layout, they should not only pursue the number of connections, but also pay attention to the quality and value of operation.
Will NB-IoT be a pioneer or a pioneer in everything? From the perspective of continuous evolution, NB-IoT is still in its early stages of development, and the problem remains unsolved. Whether 5G will fundamentally change the cellular network depends not on what to do, but on how to do it. Reviewing and rewinding the development path of NB-IoT can at least provide some reference for everything operation and take less detours.

From Value Chain to Value Network
In addition to the change from the pursuit of "connection" to the evaluation of "value", all operators should also be aware that the entire value system is undergoing restructuring, from a one-way "value chain" to a multi-dimensional comprehensive "value network".
Why does the value system restructure a large area of shuffling in the era of all operators?
In previous articles, I mentioned the importance of "business flow". Some Internet of Things enterprises think they are located upstream of the industry chain and far away from end users, so the pros and cons of business flow hang high. If you still hold this view in the future, you may lose to the times even if you eventually beat all your opponents.
Ning Yu, chief strategic planning expert for Huawei Software, mentioned a book he read many years ago called Open Growth: Big Business Trends. There are many very controversial points in the book, and over time, many topics have been answered and facts have ended the discussion. One of them is that the general trend of business is gradually being confirmed from the value chain to the value network.
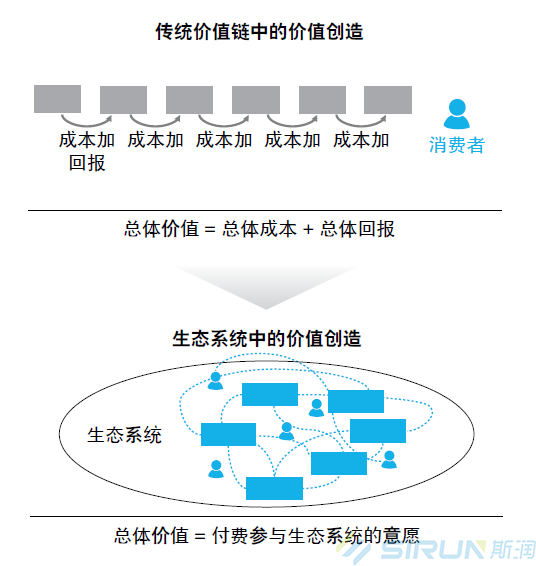
Traditionally, the value chain is one-in-one, the upper and lower boundaries of the industry are clear, the technical standards are clear, and the business model and cooperation relationship have also undergone a long-term convergence and become stable. But the success of the mobile Internet and the development of the Internet of Things are driving practitioners to break away from their traditions. They all want to be "user-centric". The closer they get to users (that is, business flow), the shorter the industry chain, the better. Moreover, technological breakthroughs have created conditions for this disruptive vision.
Each link of the industrial chain is expected to become a leader in integrating others, so that technical standards can be set in favor of the end customers. This competition will break the original industrial order, and the end result may be two ways of expression: rebuilding the industrial chain in production and manufacturing; Network in business model.
Not only may one link skip intermediate links or even establish links with end users, but it can also provide products for other traditional industrial chains. The networking of this industry has brought more room for imagination and development for the application of the Internet of Things in all walks of life, and has also provided conditions for the innovation of cooperation modes.
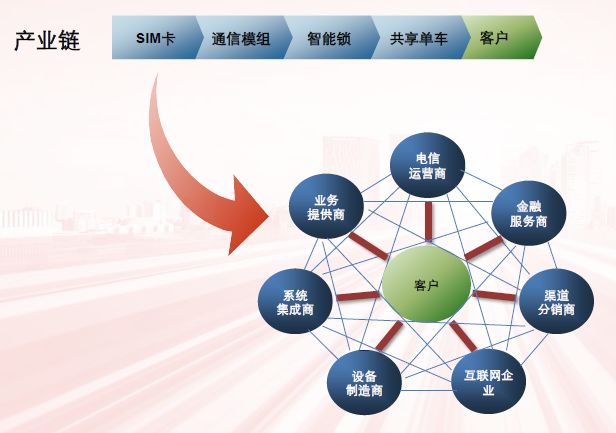
In the B2B world, the future is not necessarily a simple trading relationship. Each unit of the value network may find new opportunities and spark new sparks in cross-platform collisions. We take the automotive industry chain as an example.
In the traditional automotive value chain, the value is mainly linked to the vehicle and controlled by OEM, the original equipment manufacturer. Additional value is included in affiliated products and services, including suppliers, dealer networks, tires and car maintenance service providers, gas stations, car parts stores, insurance companies, etc. Value creation is focused on product differentiation and support services, including upgrade options such as leather interiors and shades, as well as safety ratings and brand exclusiveness.
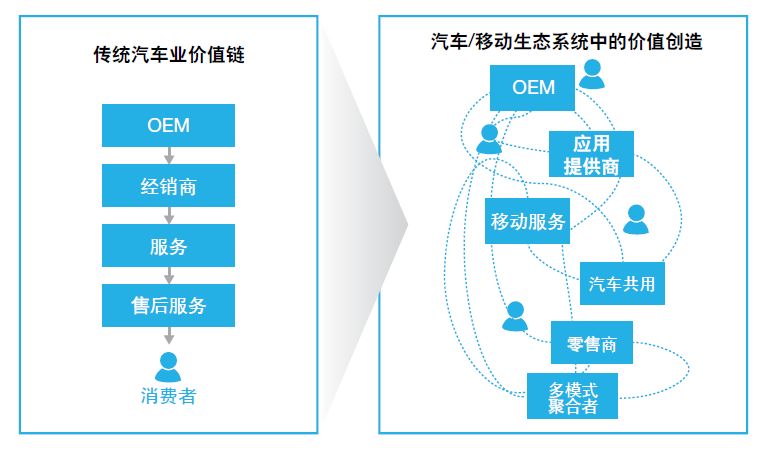
In the new automobile/mobile ecosystem, value will be linked to the benefits consumers get from the entire mobile experience and related services, not from the inherent value of the automobile itself as a vehicle. Value creation reflects the quality of the entire customer experience. The better the customer experience, the more value will be created.
Support services (such as SiriusXM for satellite broadcasting), remote services (such as OnStar), or high-speed connections improve the entertainment experience of travel and provide greater convenience to consumers. Because experience creates greater value, consumers may be more willing to pay. Value may also shift from car manufacturers and dealers to mobile ecosystem coordinators. All kinds of manufacturers have the opportunity to participate in a branch role of Universal Operators.
We have long gone out of panic and panic and become accustomed to the bombardment of new technologies and concepts. Subversive discussions are endless, but what is really possible and what will eventually happen is the best of the best. Rather than talk about subversion, think gradually, and the future will ultimately be different from the old days, either constantly redefining itself or constantly being redefined by others. It is time for innovative enterprises or those trying to embrace the Internet of Things to accept the barbarbarians at their doors in an open manner, keep in close contact with new ecosystems and partners, and think about what to do next.
This article was inspired by a speech by Ning Yu, the Chief Strategic Planning Expert for Huawei Software, entitled "The fragmented Internet of Things calls for a more open ecology". Thank you very much.
This article summarizes:
1. When an Internet of Things enterprise no longer only pursues selling products to users, but continuously provides various kinds of additional services on the original basis, and continuously generates new service content and income methods, it has the basic conditions to become a "everything operator".
2. When all operators layout, they should not only pursue the number of connections, but also pay attention to the quality and value of operation.
3. The value system of the Internet of Things is undergoing rebuilding, evolving from chain to network. In the B2B world, the future is not necessarily a simple business relationship. Each unit of the value network may find new opportunities and burst new sparks in cross-platform collisions.
(The above illustrations are from the Public Number Internet of Think Tank)

 京公网安备 11010602103187号
京公网安备 11010602103187号










